Probabilities of Counting Codes
Автор: Peter Müller
2011
Переплёт: Мягкая обложка, 114 страниц
Категория: Научная литература
ISBN: 9783842380387
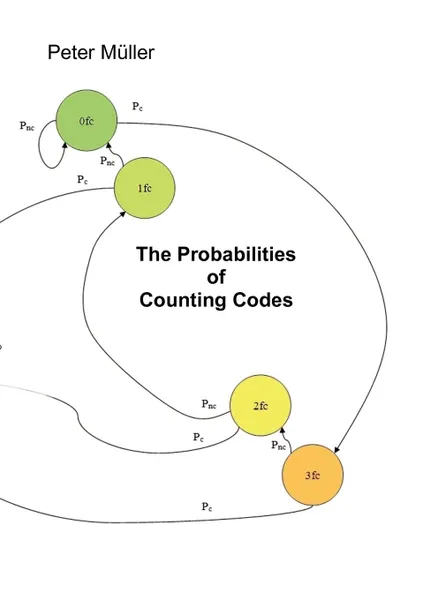
📕 In many cases counters are used to count special events within an endless sequence of events. This paper discusses a specific calculation, related to the probability of a counter overrun if the special event occurs not in a predictable way but with a certain probability.
Different counter codes are compared with each other.
A probability formula is developed for special scenarios which are normally analyzed by state diagrams and which can be numerically solved by the related Markov chains.
The target is to enable a non-numerical discussion of the topic.
It is shown how formulas can be found based on the rules of the probability theory, and their correctness is verified by a comparison with Markov chains.
Different counter codes are compared with each other.
A probability formula is developed for special scenarios which are normally analyzed by state diagrams and which can be numerically solved by the related Markov chains.
The target is to enable a non-numerical discussion of the topic.
It is shown how formulas can be found based on the rules of the probability theory, and their correctness is verified by a comparison with Markov chains.
Мнения